

Tree to 25 m (80 ft) tall and 50 cm (20 in) diameter, with open crown of spreading branches. Bark gray, smoothish, becoming black and deeply furrowed into thick rough ridges and plates. Inner bark orange or dark yellow. Twigs brown, hairy when young, ending in a cluster of large 5-angled brown to gray hairy buds. Leaves alternate, elliptic, 10-23 cm (4-9 in) long, 8-15 cm (3.7-6 in) wide, deeply divided into 7-9 tapering lobes ending in several bristle-tipped teeth, sinuses between lobes may be shallow or deep, shiny green above, yellow-green and hairy or with tufts of brown hairs in vein axils below. Fruits are acorns maturing in the second year, egg-shaped, 15-20 mm (0.6-0.8 in) long, about 1/2 enclosed by the cup.
Distribution: Native to most of the eastern half of the U. S.
Habitat: upland oak-pine and oak-hickory forests
Comment: The lumber is marketed as red oak. Quercus is the ancient classical name for the European oaks; velutina refers to the velvety pubescence of the lower leaf surface.
NWI status: none
Distribution in Oklahoma: 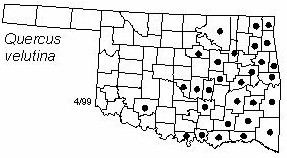
BACK
NEXT
RETURN TO INDEX
Last update: 9/17/99
 Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer