
Shrub to 7.5 m (25 ft) tall. Crown rounded. Bark light to dark gray, with bitter taste. Twigs green to red-brown; slender; pubescent; unpleasant scent when bruised. Leaves alternate or opposite, compound, trifoliate; leaflets ovate-oblong, 10-15 cm (4-6 in) long and 5-10 cm (2-4 in) wide; unpleasant aroma when crushed; pubescent and glandular below, dark green and lustrous above; cuneate at base; margins entire or finely serrate; petiole stout, leaflets nearly sessile. Inflorescence a terminal cyme of small flowers on slender pedicels; calyx lobes 4-5, obtuse, pubescent; petals 4-5, green-white, oblong, exceeding the calyx lobe; styles polygamous; pistillate flowers with raised pistils and abortive anthers; style short, stigma 2-3 lobed; stamens 4-5, alternating with petals, filaments hairy; flowers appear from March to July. Fruit a samara, 2-2.5 cm (0.8-1 in) long, thin and wafer-like, suborbicular to obovate; seeds 2-3, reddish brown; fruits mature August to September.
Distribution: Oklahoma and Texas, west to California, north to Colorado and Utah, east to Minnesota, Illinois and New York, south to Florida. Although uncommon, hoptree can be found from the southeast corner of Oklahoma to the far northwest.
Habitat: ranges from dry rocky slopes to valley bottoms.
Comments: Ptelea is the classical name for elm; trifoliata refers to the three leaflets.
Field identification: all parts of this plant have a disagreeable odor. There are four subspecies in Oklahoma: angustifolia (has narrow leaves), mollis (branches, leaflets and inflorescence are tomentose), polyadenia (has larger flowers), and trifoliata.
Horticulture: Although cultivated since 1724, hoptree is only used occasionally as an ornamental. It is often planted in shelterbelts. Hoptree can be propagated by seed, grafting, or layering.
Medicinal use: a root tincture is used to treat dyspepsia and as a mild tonic in tropics. Contains the alkaloid berberine.
Food use: fruits used as a hops substitute, hence the common name.
Wildlife value: Hoptree is of limited use for wildlife.
NWI status: UPL,FAC.
Distribution in Oklahoma: 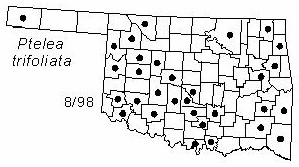
BACK
NEXT
RETURN TO INDEX
Last update: 9/15/99
 Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
Go to Oklahoma Biological Survey Home Page
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer